Outer dia φ1.9mm Length 350mm
Thermal Resistance Temperature Sensor Manufacturers
A thermal resistance temperature sensor is a kind of sensor thermometer that uses the principle that the resistance value of a conductor or semiconductor changes with temperature. Thermal resistance temperature sensors are divided into two categories: metal thermal resistance and semiconductor thermistors. Thermal resistors are widely used to measure temperatures in the range of -200 ~850°C.
| Type | PT10, PT50, PT100, PT200, PT500, PT1000, Cu50, Cu100, Cu200, Cu500, Cu1000, etc. |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 850°C |
| Accuracy | A level, B level, C level |
| Response Time | 1 second to 30 seconds |
-
-
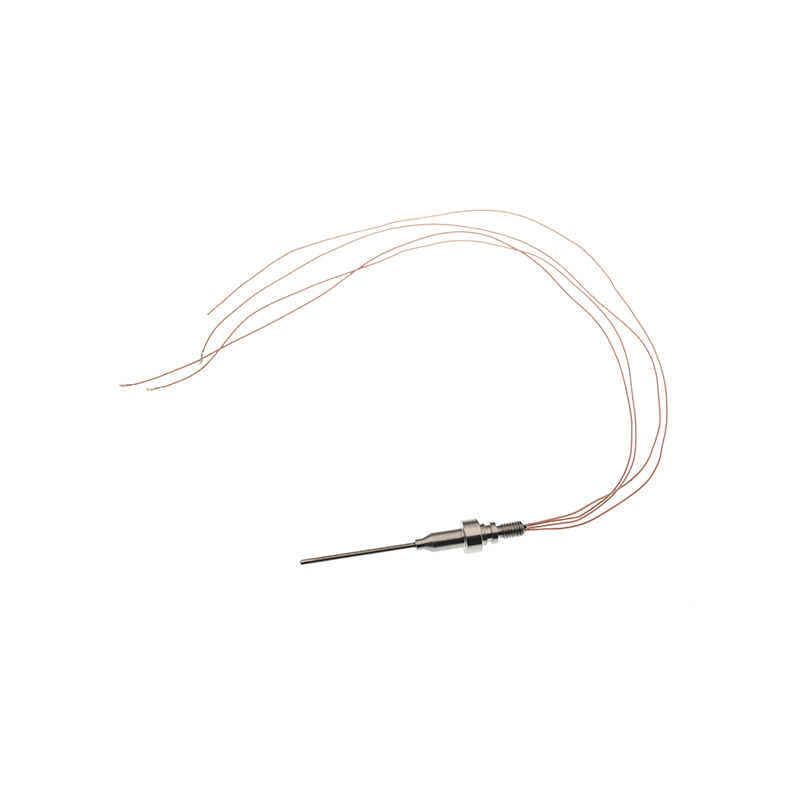 Marine PT100 temperature sensor
Marine PT100 temperature sensorProduct item No.: SKT-2045 Temperature measuring element Pt100 Resistance value 0℃, 100 Ω Mea...
-
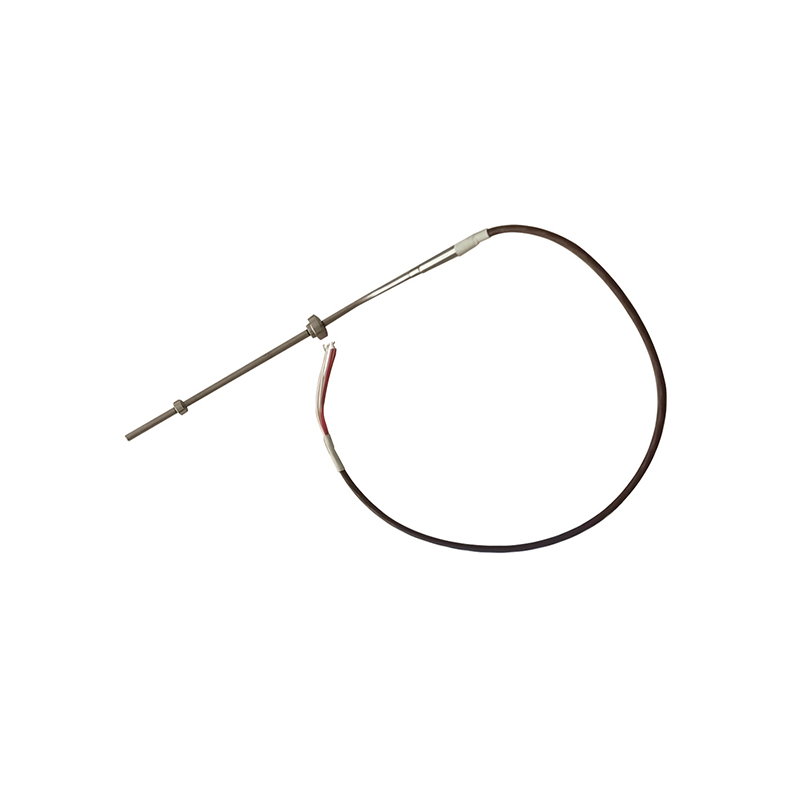 Multi-point exhaust temperature sensor
Multi-point exhaust temperature sensorProduct item No.: SKT-2572 Wire High-temperature resistant wire Thermal resistance type & ...
-
 Multi-point exhaust temperature sensor
Multi-point exhaust temperature sensorProduct item No.: SKT-2573 Wire High-temperature resistant wire Thermal resistance type & ...
-
 Temperature sensor
Temperature sensorProduct item No.: SKT-2574 Product accuracy B(25/85)=3970K±1% R(25 ℃ ) 4.95~5.05KΩ R(-40 ℃ )...
-
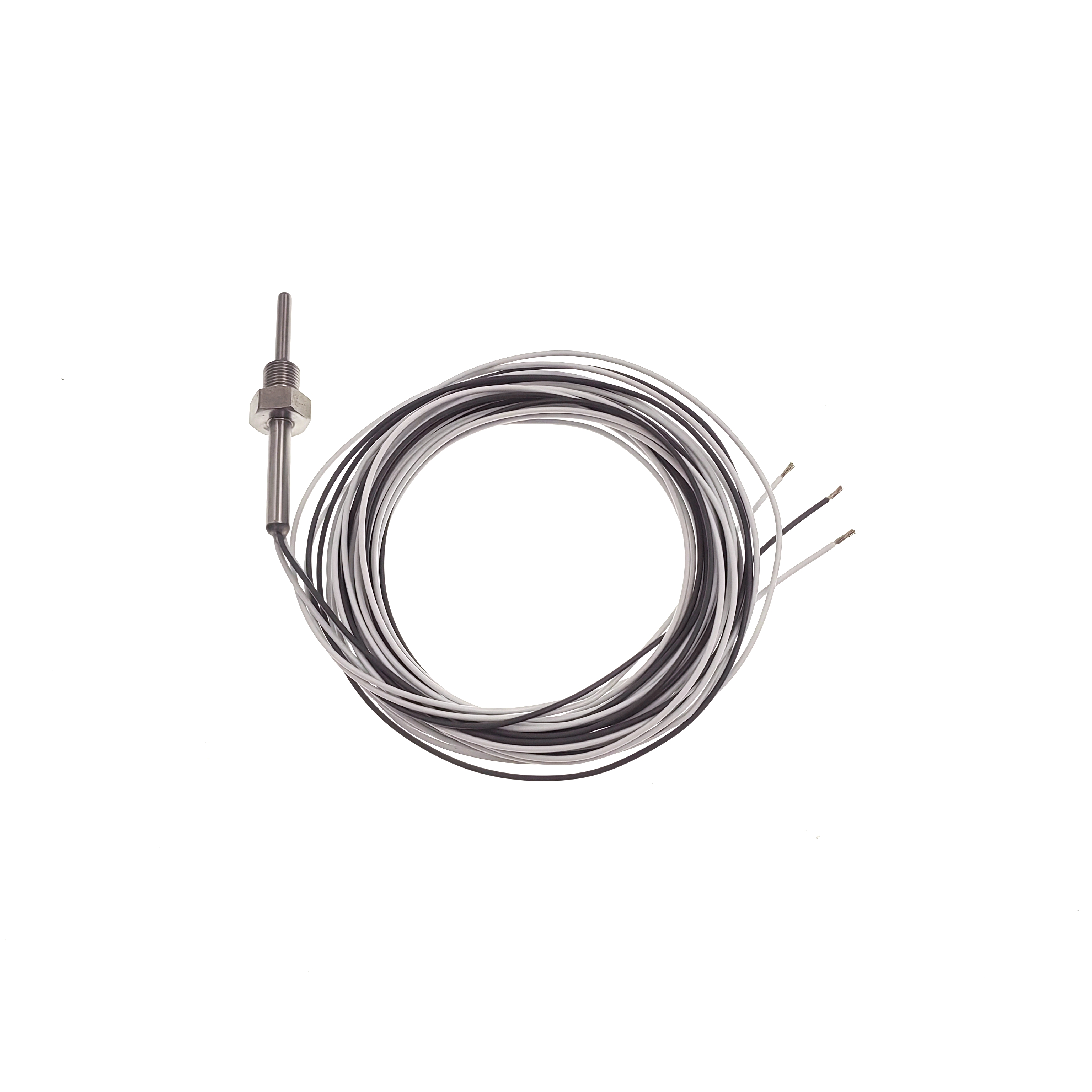 PT100 thermal resistance
PT100 thermal resistanceProduct item No.: SKT-2673 Temperature measuring element PT100 Temperature measuring range -20...
-
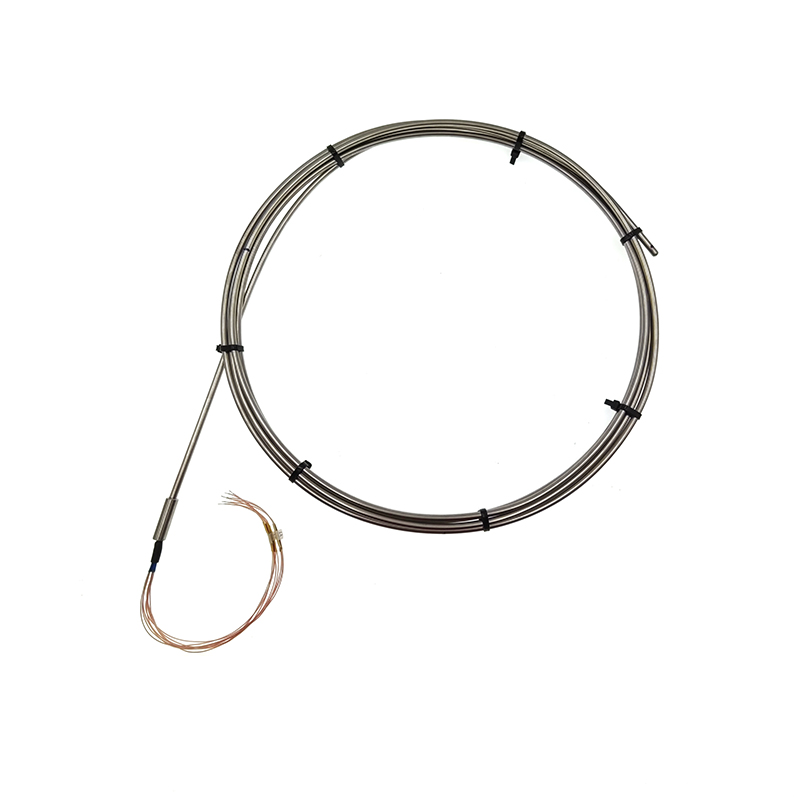 PT100 thermal resistance Integrated Multi-point Armored Temperature Sensor
PT100 thermal resistance Integrated Multi-point Armored Temperature SensorProduct item No.: SKT-2677 Temperature measuring element & q'ty PT100 x 3 Accuracy Class A...
-
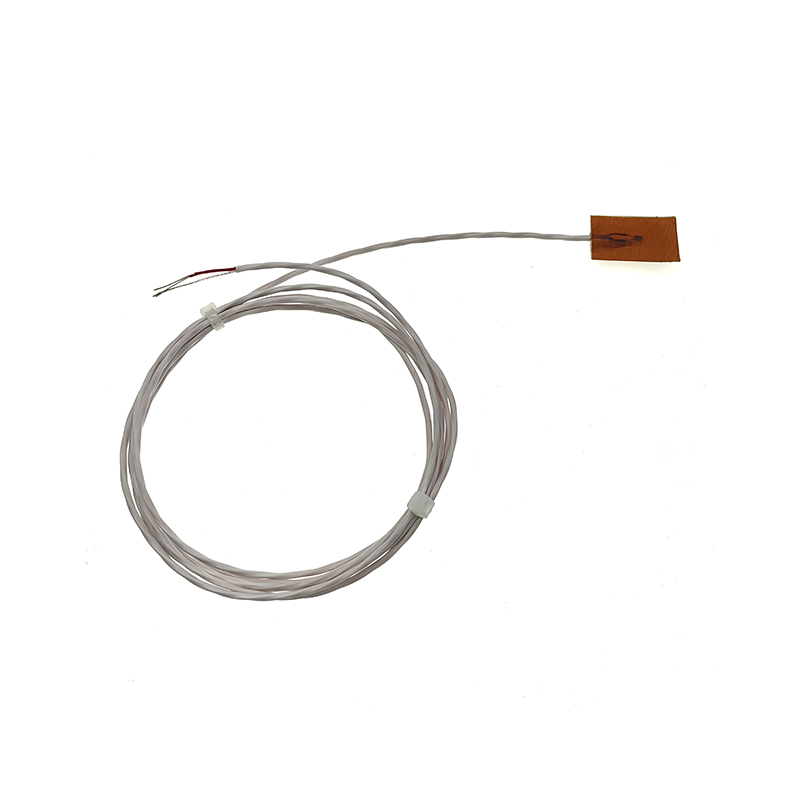 Self-adhesive PT100 surface mount temperature sensor
Self-adhesive PT100 surface mount temperature sensorProduct item No.: SKT-2690 Temperature measuring element PT100 Accuracy Class A Temperature...
-
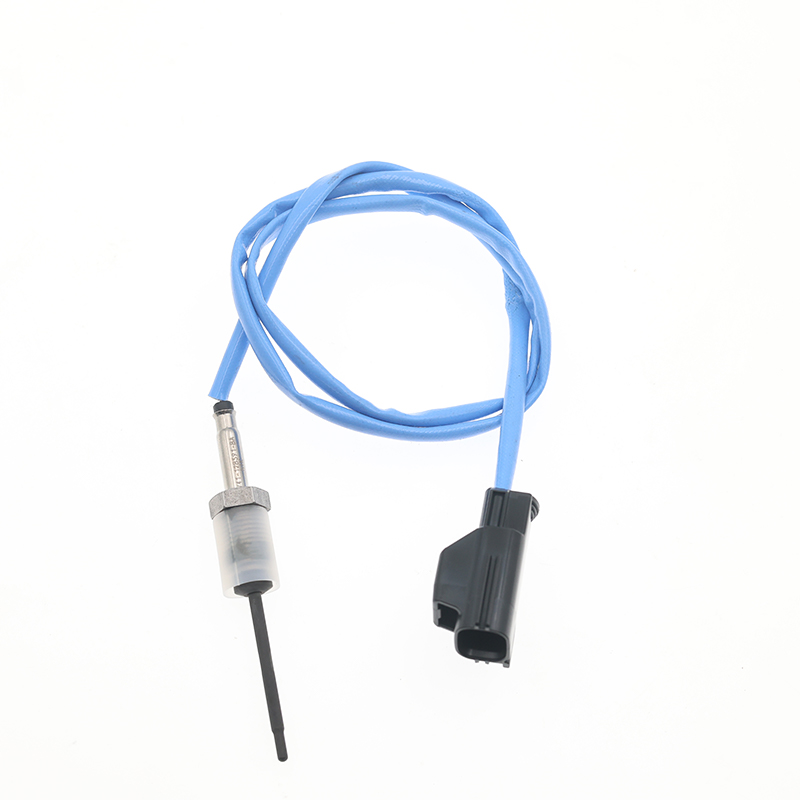 1797768 AV4112B591BA Thermistors Temperature Sensors
1797768 AV4112B591BA Thermistors Temperature SensorsSKT-947 SOOK# SKT-947 OE# 1797768 AV4112B591BA Application Ford Kuga, CBS
-
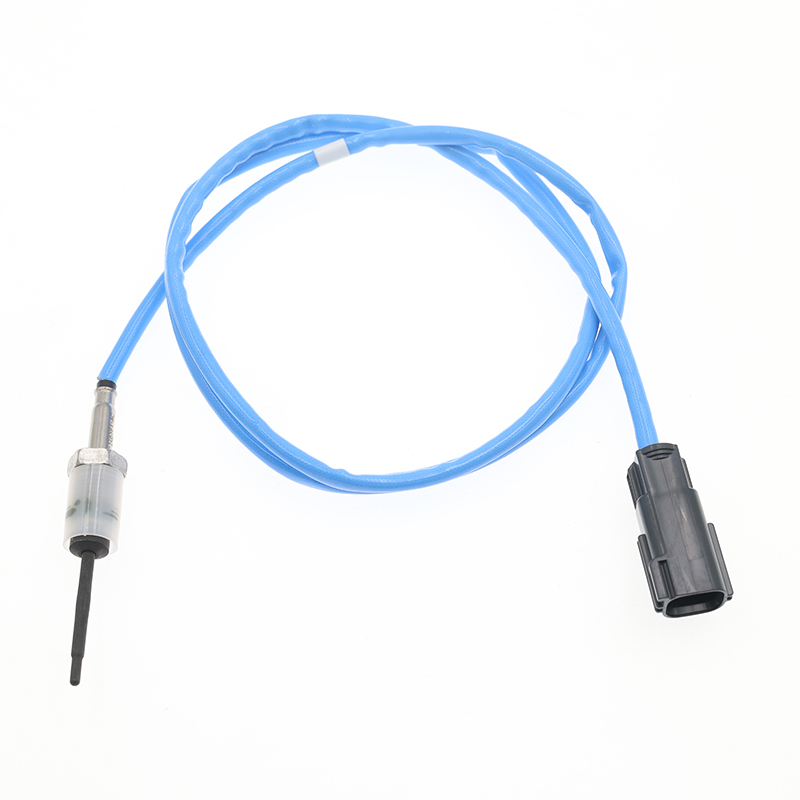 FV61-12B591-AC FV6112B591AC 1939835 https://www.sook-sensors.com/product/thermistors-temperature-sensors/1797768-av4112b591ba-thermistors-temperature-sensors.html
FV61-12B591-AC FV6112B591AC 1939835 https://www.sook-sensors.com/product/thermistors-temperature-sensors/1797768-av4112b591ba-thermistors-temperature-sensors.htmlSKT-1396 SOOK# SKT-1396 OE# FV61-12B591-AC FV6112B591AC 1939835 Application FORD FOCUS MK3 ...
-
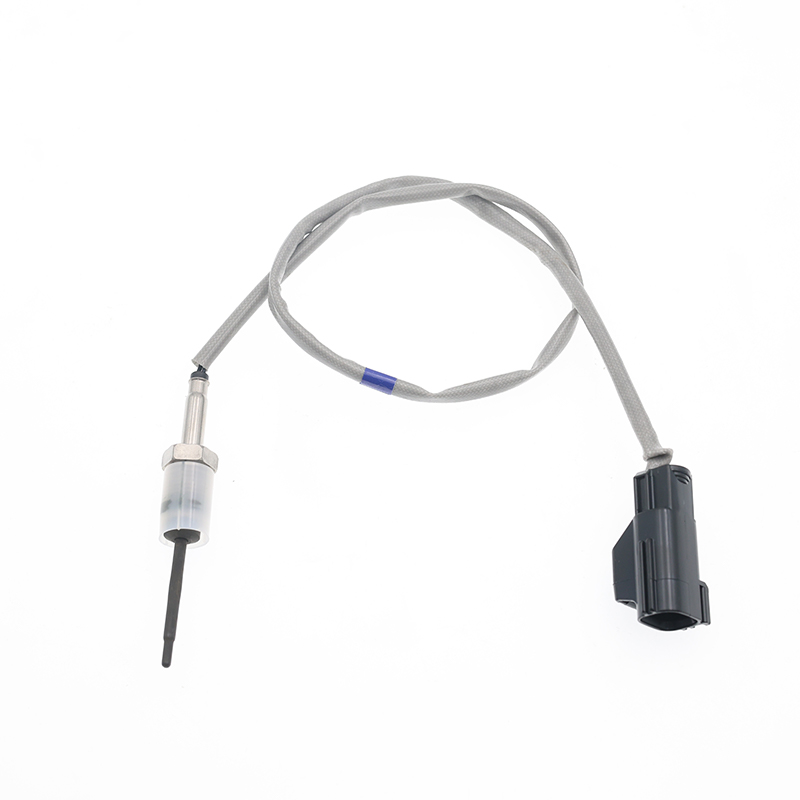 GK3112B591BB GK3112B591CA Thermistors Temperature Sensors
GK3112B591BB GK3112B591CA Thermistors Temperature SensorsSKT-1470 SOOK# SKT-1470 OE# GK3112B591BB GK3112B591CA Application FORD TRANSIT MK4
-
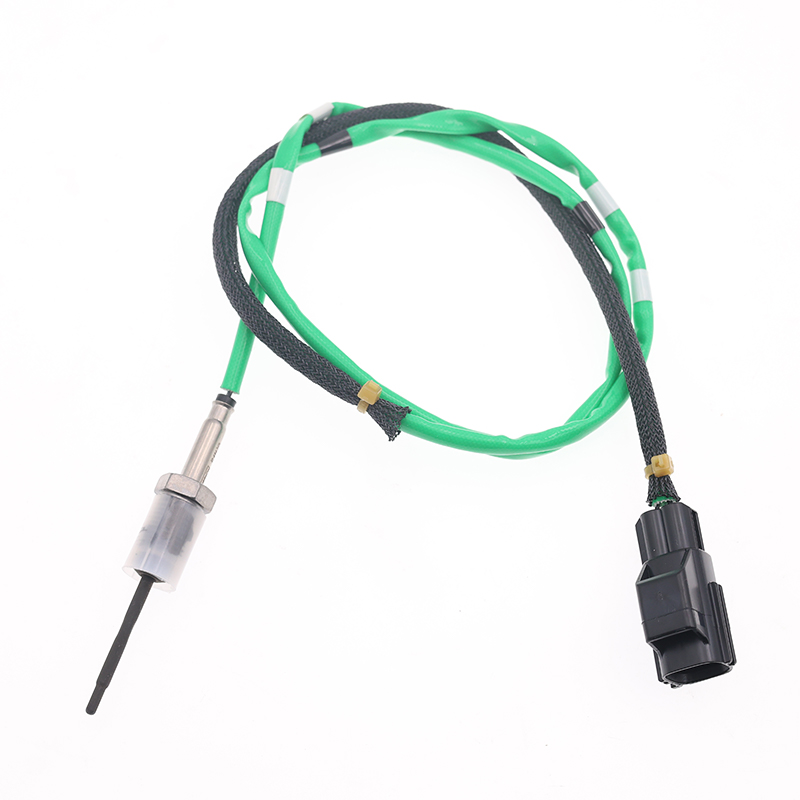 EB3G12B591DC EB3G-12B591-DC Thermistors Temperature Sensors
EB3G12B591DC EB3G-12B591-DC Thermistors Temperature SensorsSKT-1815 SOOK# SKT-1815 OE# EB3G12B591DC EB3G-12B591-DC Application FORD RANGER T6 MK3
Sook High Tech (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. was established in 2015, with a registered capital of 30.5 million yuan. Has won High-tech enterprise, National science and technology small and medium-sized enterprise, Software enterprise, Member of China Machinery Industry Standardization Technology Association, Council Members of Sensor and IoT Industry Association, Council Members of China Instrument Industry Association Sensor Branch and Council Members of Jiangsu Import and Export Chamber of Commerce.
As a professional China OEM Thermal Resistance Temperature Sensor Manufacturers and ODM Thermal Resistance Temperature Sensor-RTD Factory
, SOOK High Tech focuses on the design, production, sales and integration of various sensors for smart cars and industrial fields, as well as cables and heaters for the industrial field.
Has an annual production capacity of 600,000 sensors of various types. There are more than 2,000 items of exhaust temperature sensors, 450 items of NOx sensors, and 1,300 items of ABS sensor, which are exported to Europe and the United States.
Learn about our industry exhibition information and recent events in our company.
-
What Is a NOx Sensor and Why Is It So Important in Modern Vehicles?
If you work with modern diesel vehicles—or you're responsible for engines, aftertreatment systems, or emission compliance—you’ve probably heard customers ask: "What exactly is a NO...23 -
What is an NTC EGT Sensor?
In the fields of automotive and industrial measurement, the NTC EGT sensor is another widely utilized tool for monitoring exhaust gas temperatures. 1. Definition and Core Principle...16 -
Why are PTC sensors more accurate than ordinary sensors?
In automotive emission monitoring and high-temperature industrial operations, the precision of an Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) sensor directly impacts engine efficiency and safety...09 -
What is the specific role of the PTC EGT Sensor in DPF regeneration?
The Specific Role of the PTC EGT Sensor in DPF Regeneration: 1. Real-time Temperature Monitoring The sensor is installed upstream of the DPF and collects exhaust gas temperature in...02
What are some typical applications for Thermistors Temperature Sensors in automotive electronics or portable devices?
1. Gas Turbine and Engine Exhaust Temperature Monitoring
K-type thermocouples, due to their wide temperature measurement range (-200°C to 1250°C) and excellent oxidation resistance, are commonly used for real-time exhaust temperature monitoring in gas turbines, aircraft engines, and automotive engines, helping to optimize combustion efficiency and provide fault warnings.
2. Metallurgy and Metal Heat Treatment
In the heat treatment of metals such as steel and aluminum alloys, precise control of the furnace temperature profile is essential. K-type thermocouples maintain stable output in high-temperature environments, making them the preferred sensor for critical locations such as furnace temperatures, heat treatment furnaces, and forging dies.
3. Petrochemical and Chemical Process Control
Petroleum refining and chemical reactors often involve high-temperature, corrosive media. The high-temperature and corrosion-resistant properties of K-type thermocouples enable reliable temperature measurement of critical nodes such as reactors, heat exchangers, and steam pipes, ensuring production safety.
4. Industrial Furnaces and Ceramic Firing
High-temperature firing processes for ceramics, glass, and other applications require extremely high temperature uniformity. K-type thermocouples can be placed at multiple locations within the furnace to achieve multi-point temperature acquisition, helping to achieve uniform temperature control and improve product quality.
How to calibrate Thermistors Temperature Sensors?
1. Two-Point Calibration: Select two known temperature points (e.g., 0°C and 70°C), measure the corresponding resistance values, and use a logarithmic model to determine the β coefficient, achieving a calibration accuracy of ±0.03°C.
2. Three-Point Calibration: Measure at low, medium, and high temperatures (e.g., -40°C, 25°C, and 125°C). This method further improves linearization accuracy and is suitable for automotive or industrial sensors with a wide temperature range.
3. Using the Steinhart-Hart equation: Solve the equation coefficients at four or more temperature points to achieve higher fitting accuracy. This method is commonly used in scientific research and for high-precision instrument calibration. 4. Batch sampling calibration: Only a small number of samples are taken from a large number of thermistors in the same batch for complete calibration. Statistical methods are used to estimate the overall error range to achieve a balance between cost and accuracy.


 English
English Español
Español Français
Français
 简体中文
简体中文


