Mack LEU 2011-08 Mack MRU 2011-08
Thermocouple EGT Sensor Manufacturers
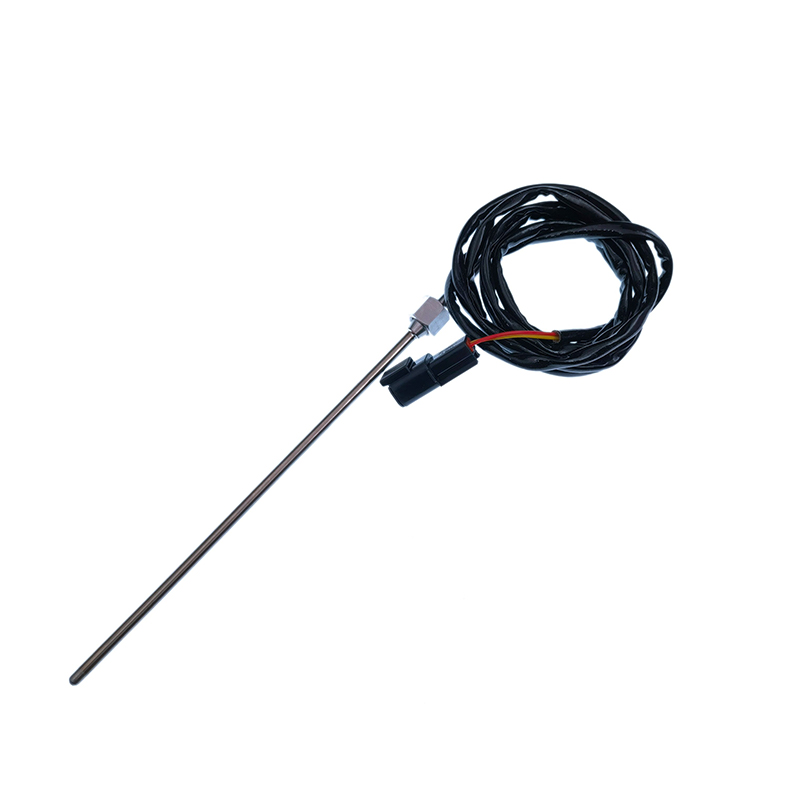
Thermocouple EGT Sensor supports continuous measurement from -40°C to 1000°C, meeting the needs of high-temperature scenarios and ensuring structural stability and measurement accuracy under extremely high temperatures. The mineral-insulated alloy sheath design, combined with a special sealing ring, effectively resists mechanical vibration, particle erosion, and chemical corrosion, extending service life. Unique packaging and welding technology ensure the long-term stability of the sensor in high-vibration environments such as gas turbines. The small-sized probe of the thermocouple exhaust temperature sensor is matched with an armored structure to reduce thermal inertia and ensure sensitive capture of temperature changes.
| Sensor Type | 1~4 |
| Probe Numbers | K/N/E Type |
| RTD Type | PWM/LIN/CAN |
| Operating Temp. Range | -40℃ to +1200℃ |
| Measurement Accuracy | <600℃:±5℃ |
| >600℃:±10℃ | |
| Response Time at 10m/s | <6s |
| Design Reliability | Excellent |
-

-

-

-

-
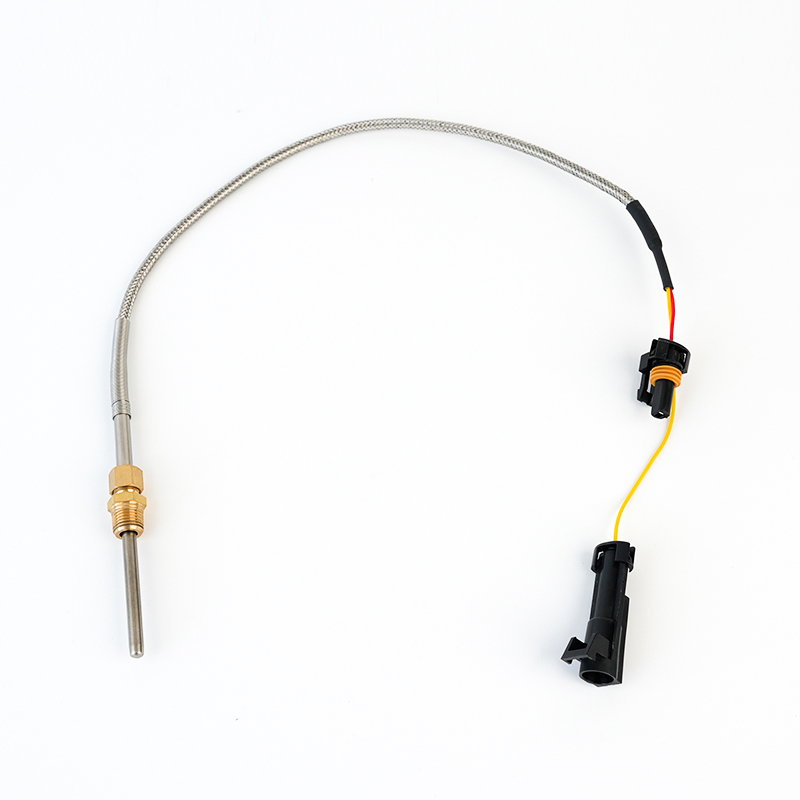
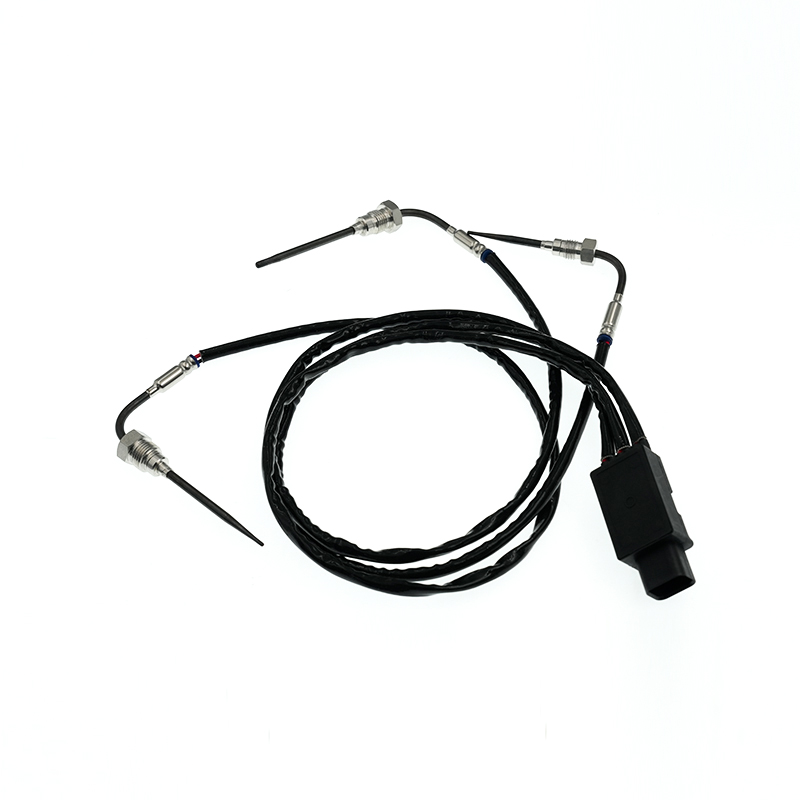 RE545199 Thermocouple EGT Sensor
RE545199 Thermocouple EGT SensorJohn Deere
-
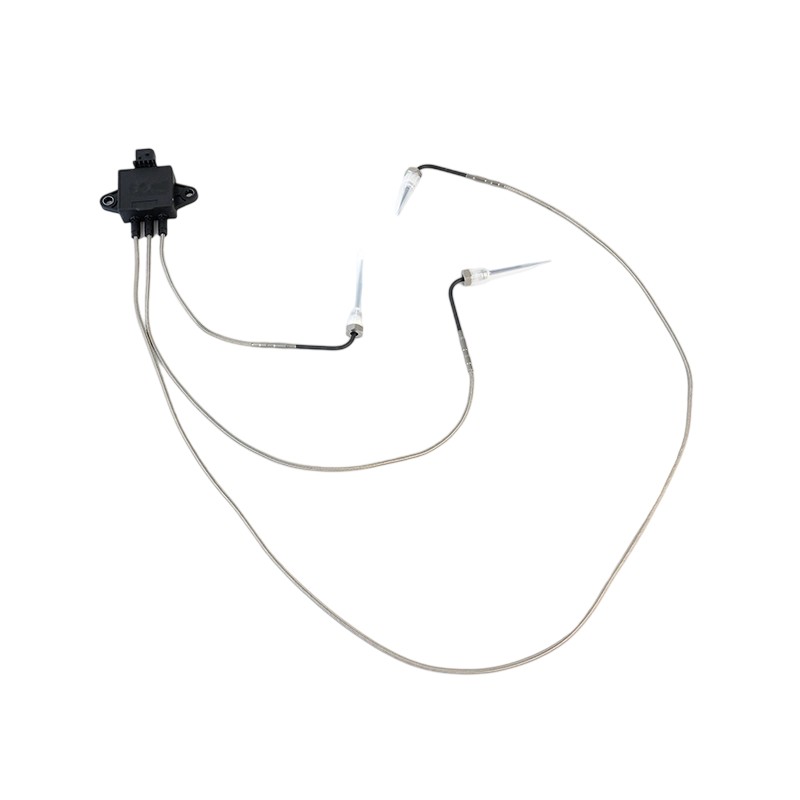
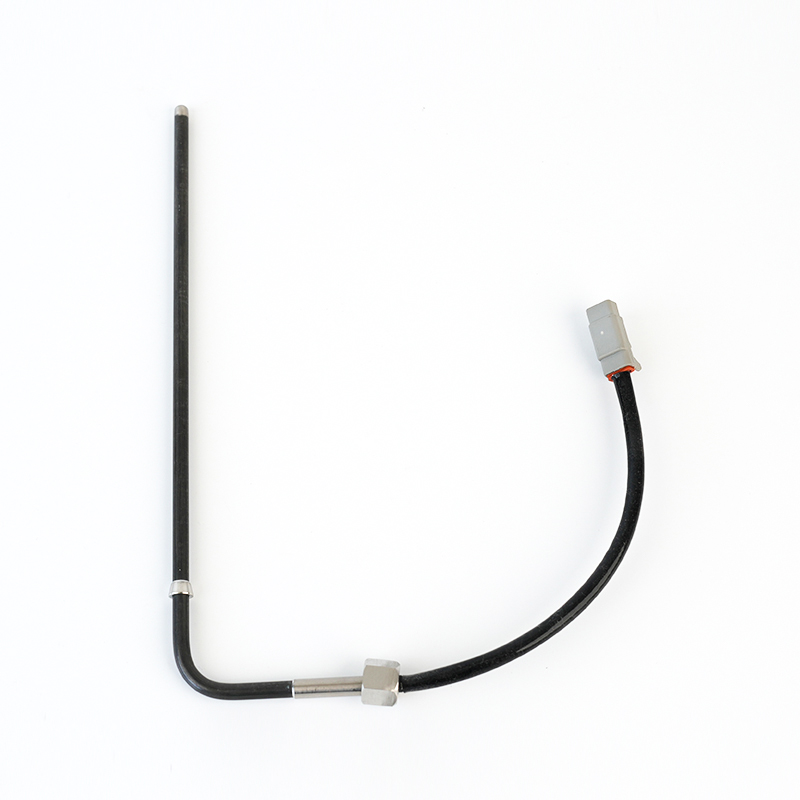
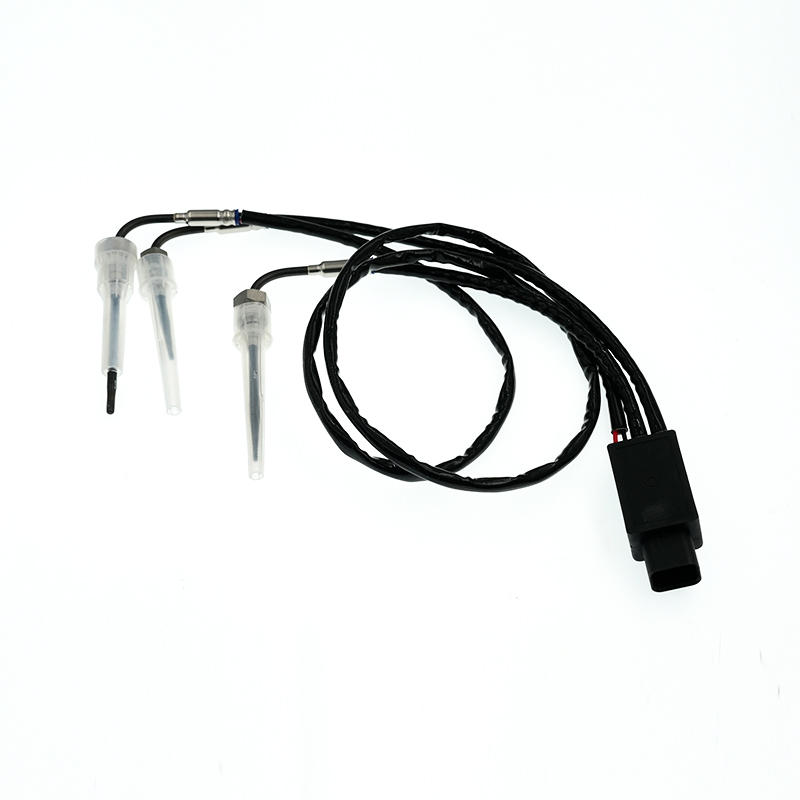 RE545198 Thermocouple EGT Sensor
RE545198 Thermocouple EGT SensorJohn Deere
-
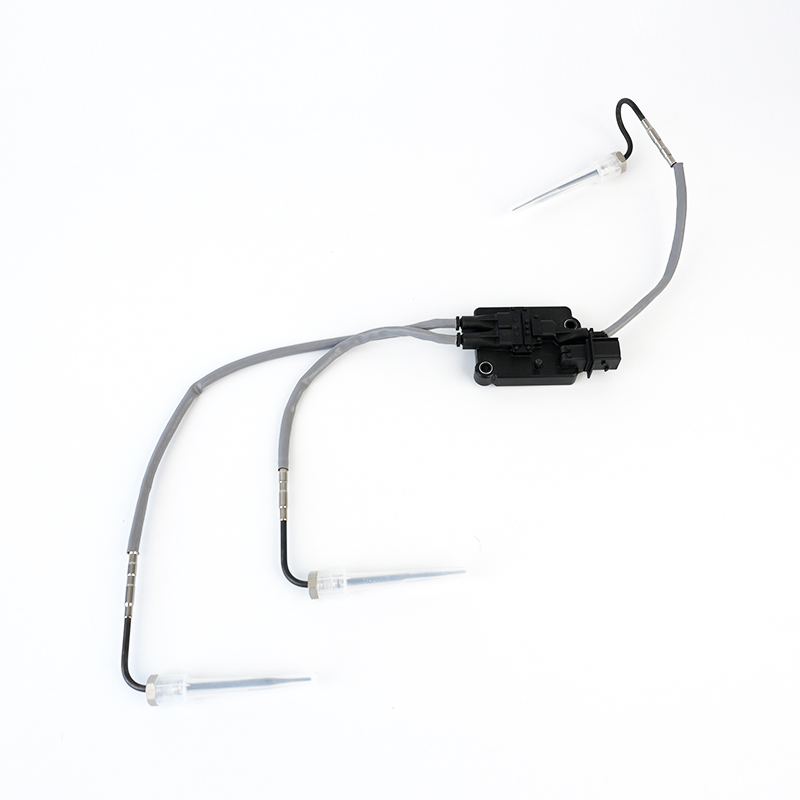
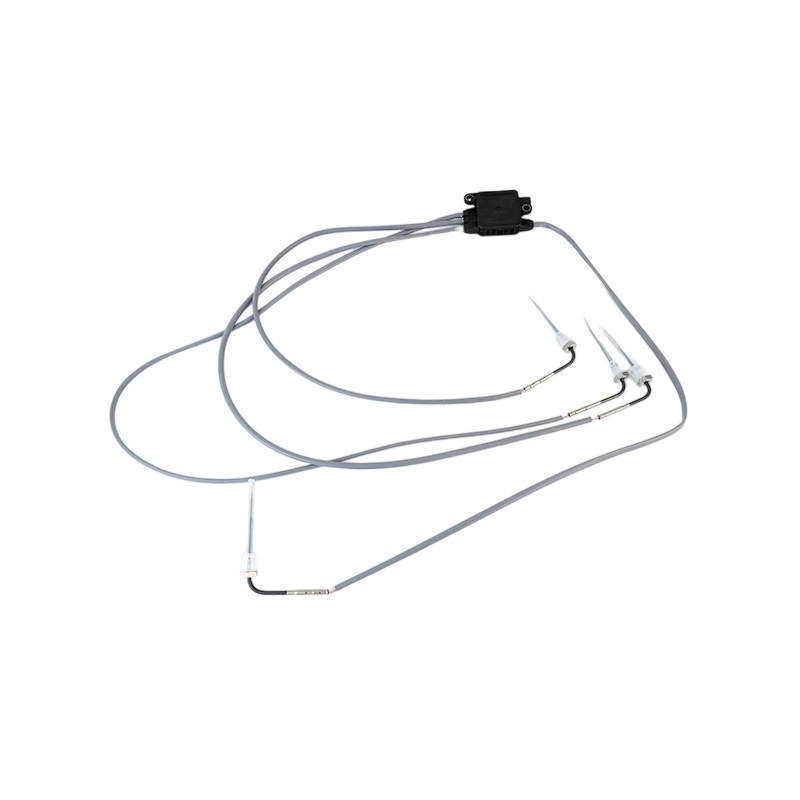
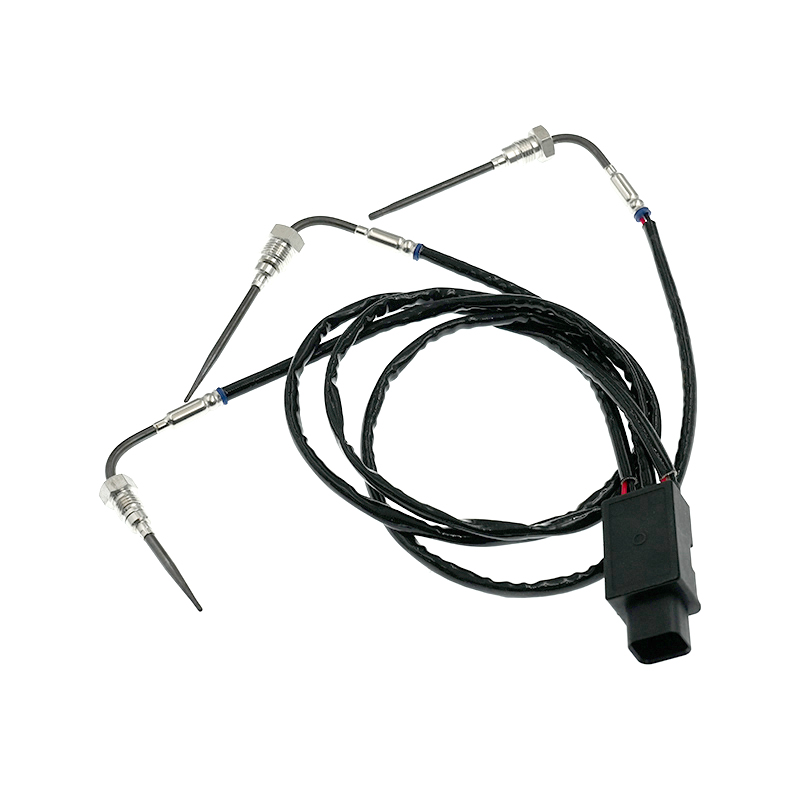 RE544555 Thermocouple EGT Sensor
RE544555 Thermocouple EGT SensorJohn Deere
-
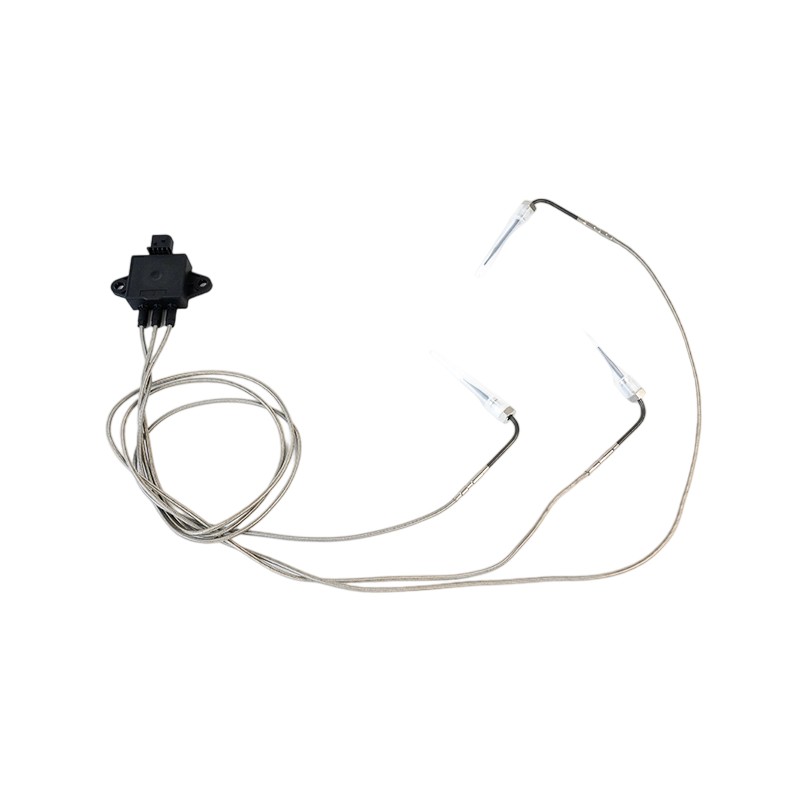
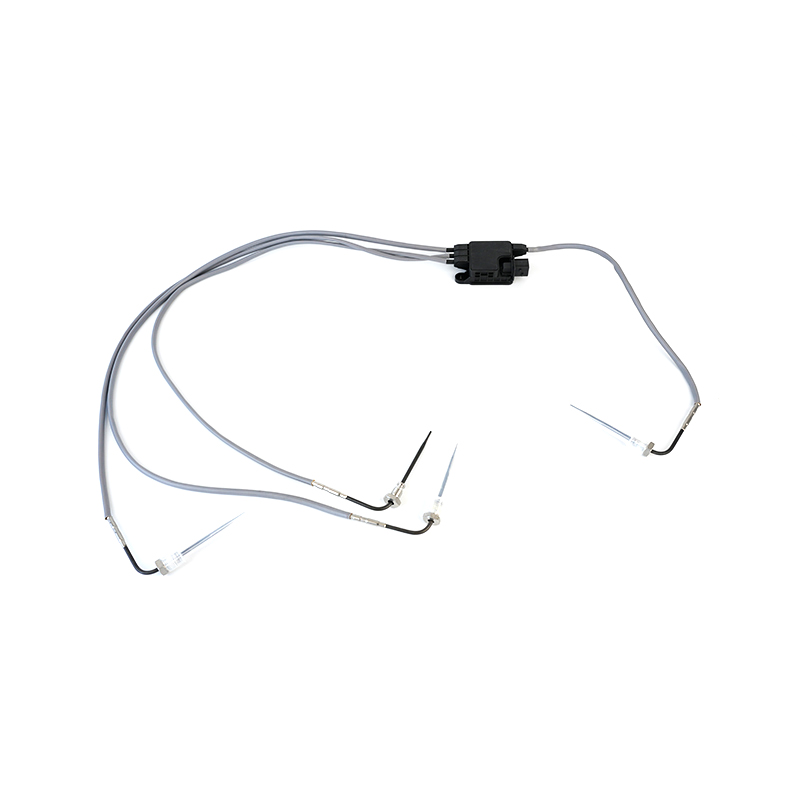
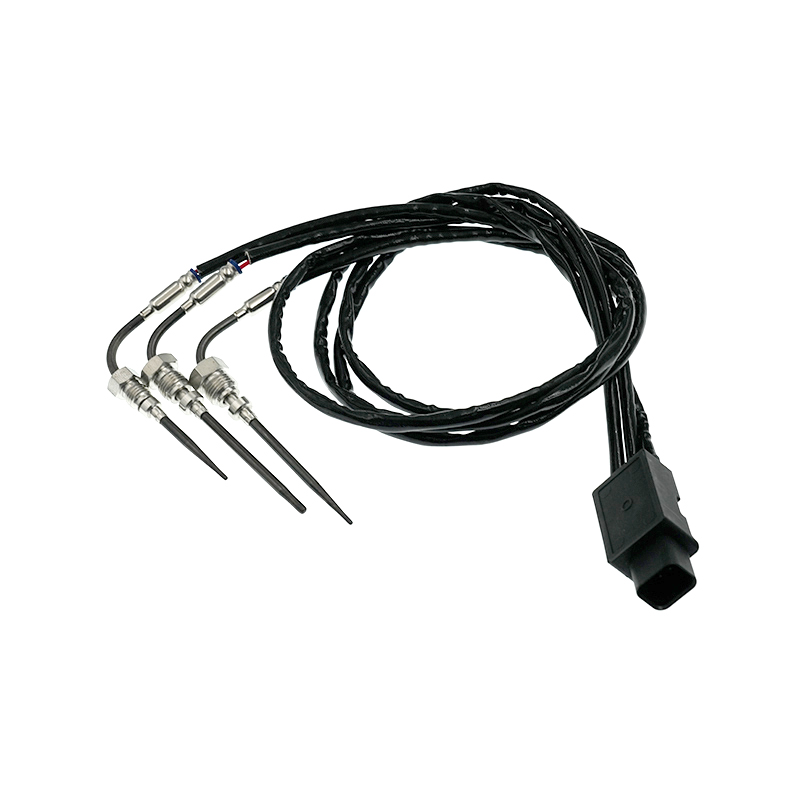 RE542440 Thermocouple EGT Sensor
RE542440 Thermocouple EGT SensorJohn Deere
-

-

-

-

Sook High Tech (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. was established in 2015, with a registered capital of 30.5 million yuan. Has won High-tech enterprise, National science and technology small and medium-sized enterprise, Software enterprise, Member of China Machinery Industry Standardization Technology Association, Council Members of Sensor and IoT Industry Association, Council Members of China Instrument Industry Association Sensor Branch and Council Members of Jiangsu Import and Export Chamber of Commerce.
As a professional China OEM Thermocouple EGT Sensor Manufacturers and ODM Thermocouple EGT Sensor Factory
, SOOK High Tech focuses on the design, production, sales and integration of various sensors for smart cars and industrial fields, as well as cables and heaters for the industrial field.
Has an annual production capacity of 600,000 sensors of various types. There are more than 2,000 items of exhaust temperature sensors, 450 items of NOx sensors, and 1,300 items of ABS sensor, which are exported to Europe and the United States.
Learn about our industry exhibition information and recent events in our company.
-
What Is a NOx Sensor and Why Is It So Important in Modern Vehicles?
If you work with modern diesel vehicles—or you're responsible for engines, aftertreatment systems, or emission compliance—you’ve probably heard customers ask: "What exactly is a NO...23 -
What is an NTC EGT Sensor?
In the fields of automotive and industrial measurement, the NTC EGT sensor is another widely utilized tool for monitoring exhaust gas temperatures. 1. Definition and Core Principle...16 -
Why are PTC sensors more accurate than ordinary sensors?
In automotive emission monitoring and high-temperature industrial operations, the precision of an Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) sensor directly impacts engine efficiency and safety...09 -
What is the specific role of the PTC EGT Sensor in DPF regeneration?
The Specific Role of the PTC EGT Sensor in DPF Regeneration: 1. Real-time Temperature Monitoring The sensor is installed upstream of the DPF and collects exhaust gas temperature in...02
How does the Thermocouple EGT Sensor work?
1. The Seebeck Effect Generates Thermoelectric Potential
A thermocouple consists of two dissimilar metal wires connected at the measuring junction. When a temperature difference occurs between the measuring junction and the reference junction, an electromotive force (thermoelectric potential) proportional to the temperature difference is generated. This voltage signal is the source of temperature information.
2. Conversion of Thermoelectric Potential to Temperature
Using a known thermoelectric potential-temperature correspondence table (or standard function), the instrument converts microvolt-level voltages into corresponding temperatures, enabling continuous measurement. This process requires no external power, making it a self-powered sensor.
3. Cold Junction Compensation Ensures Accurate Measurements
The reference junction (cold junction) is typically maintained at a known temperature (such as room temperature). Cold junction compensation is performed internally in the instrument to eliminate the effects of cold junction temperature variations on measurement results.
4. Structural Design Enhances High-Temperature Reliability
Sook High Tech's Thermocouple EGT Sensor utilizes a mineral-insulated alloy sheath and a specialized sealing ring. This ensures structural stability in extreme environments ranging from -40°C to 1000°C, resisting mechanical vibration, particle erosion, and chemical corrosion, extending its service life. What are the differences between a Thermocouple EGT Sensor and other temperature sensors (RTDs, Thermocouples)?
1. Temperature Measurement Range
Thermocouples (including Thermocouple EGT Sensors) cover a wide temperature range of -200°C to 2300°C, making them suitable for extreme applications such as high-temperature gases and gas turbines.
RTDs (Platinum Resistance Detectors) typically measure temperatures between -200°C and 850°C, offering high accuracy but unsuitable for extremely high temperatures.
Thermocouples (NTCs/PTCs) have a narrower temperature range and are typically used for low to medium temperature measurements.
2. Signal Type and Accuracy
Thermocouples output millivolt-level voltages, which have relatively low accuracy and require amplification and cold-junction compensation.
RTDs output a resistance change signal with good linearity and high accuracy, making them suitable for applications requiring stringent accuracy.
Thermocouples output a resistance change signal with high sensitivity but nonlinearity, making them suitable for cost-sensitive applications with low accuracy requirements. 3. Response Speed and Durability
Thermocouples offer a simple structure, lightweight weight, low thermal inertia, and fast response. Sook High Tech's "small probe + armored structure" further reduces thermal inertia, enabling rapid detection of temperature fluctuations.
RTDs, due to their large metal resistor body and high thermal mass, respond relatively slowly.
Thermocouples have a response speed somewhere in between due to their material properties, but are susceptible to damage in high-temperature and high-vibration environments.
4. Cost and Installation
Thermocouples offer the lowest cost and enable long-distance signal transmission, making them suitable for high-volume industrial deployment.
RTDs are more expensive and require three- or four-wire compensation wiring, making installation more complex.
Thermocouples offer the lowest cost, but their lifespan is limited in high-temperature or corrosive environments.


 English
English Español
Español Français
Français
 简体中文
简体中文


