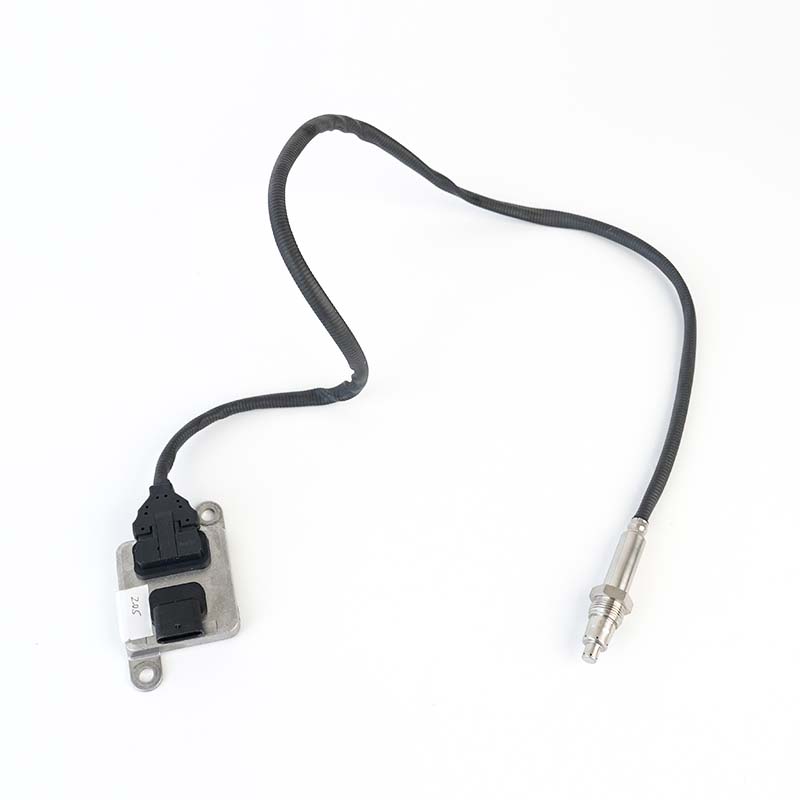
SOOK#:SKNOX205 Continenal No:5WK96788 OE#:ML239298 Application: Mitsubishi
NOx Sensor Manufacturers
Our NOx sensors are specifically designed for modern internal combustion engines and hybrid vehicles, enabling real-time monitoring of NOx concentrations in exhaust gases to ensure compliance with stringent global emission standards such as Euro 6. As a self-owned manufacturing facility, we offer end-to-end control from research and development to production and testing, delivering highly reliable and cost-effective solutions to customers.
| Range | NOx: 0~1500ppm, O₂: 12%~21% |
| Accuracy NOx | 0~100ppm: ±10ppm |
| 100~500ppm: ±10% | |
| 500~1500ppm: ±15% | |
| Accuracy O₂ | 0%~5%: ±0.25% |
| 5%~21%: ±5% | |
| Response Time | t₁₀↔90% λlin < 4900ms |
| t₁₀↔90% NOx < 5300ms | |
| Power Supply | 12V, 24V |
| Light Off Time | 120s (Devpoint to status byte OK) |
| Design Life Time | 6000h or 350,000km |
| Sensor Cable Length | 415mm, 615mm, 915mm |
| Exhaust Temperature | 800°C |
| Wire Temperature | 200°C |
| Cross Sensitivity | NO₂, NH₃, Pressure |
-

-
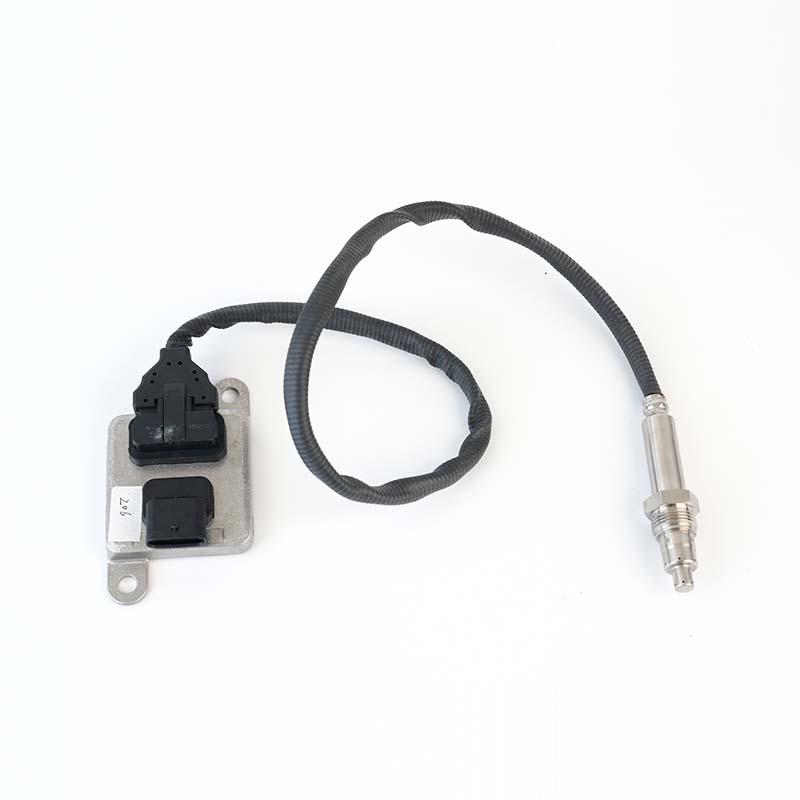 ML239299 NOx Sensor
ML239299 NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX206 Continenal No:5WK97200 OE#:ML239299 Application: Mitsubishi
-
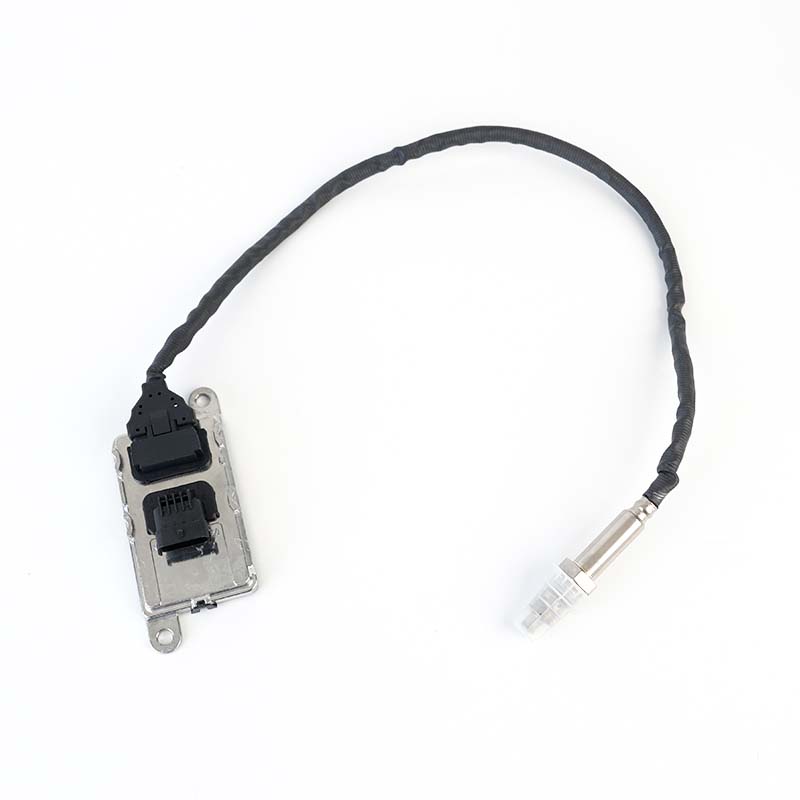 22827993 NOx Sensor
22827993 NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX207 Continenal No:5WK97371 OE#:22827993 Application: Volvo
-
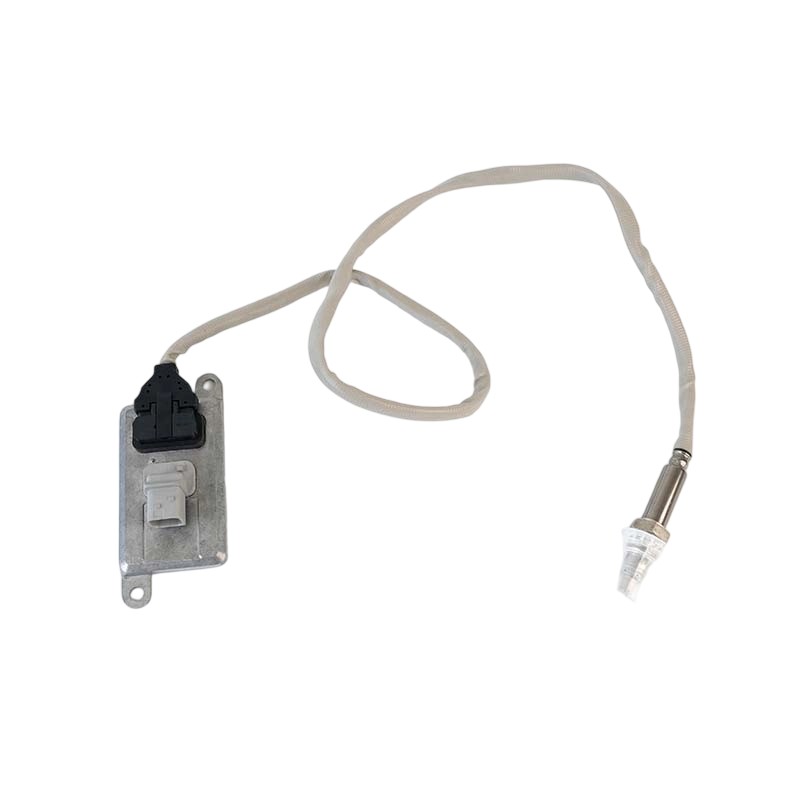 A0101539628 NOx Sensor
A0101539628 NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX217 Continenal No:5WK96659C OE#:A0101539628 Application:Mercedes-Benz
-
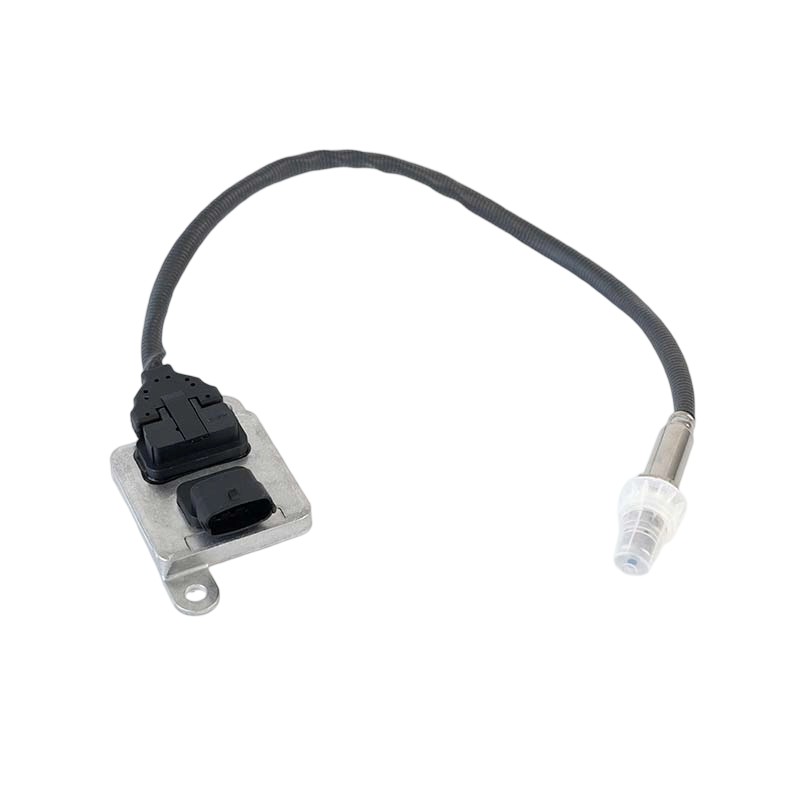 2894944RX,2894944 NOx Sensor
2894944RX,2894944 NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX224A OE#:2894944RX,2894944 Application: Cummins
-
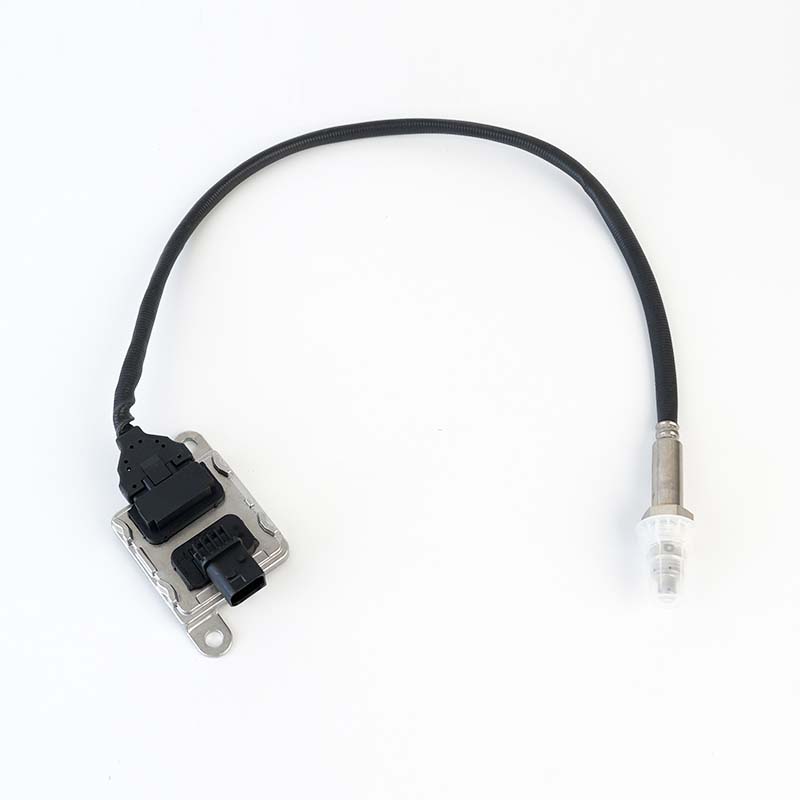 2006246,2006246PE NOx Sensor
2006246,2006246PE NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX226 Continenal No:5WK96759C OE#:2006246,2006246PE Application: DAF
-
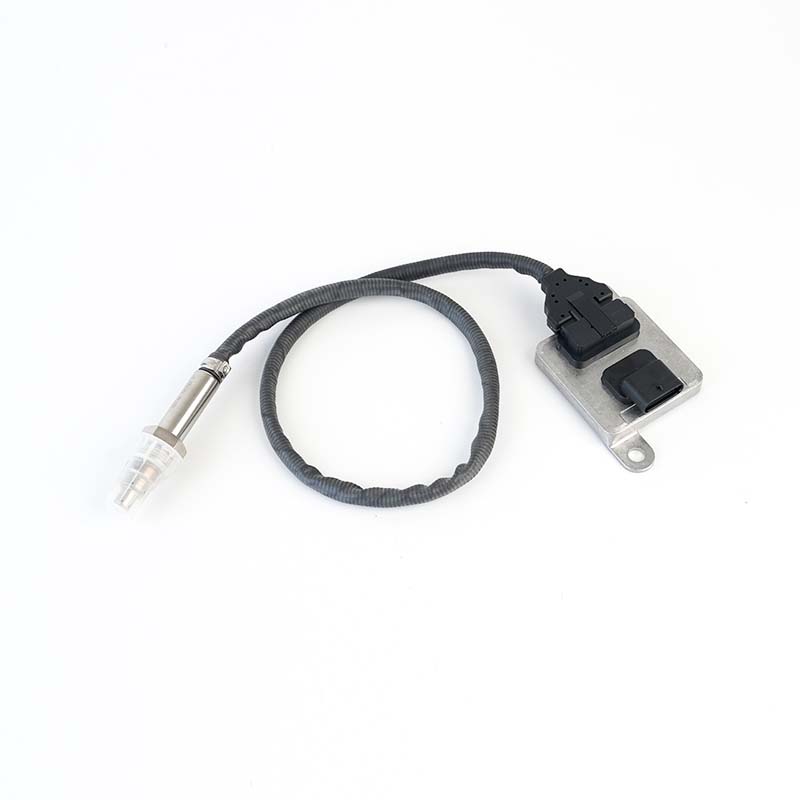 476880088,84422747 NOx Sensor
476880088,84422747 NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX328 Continenal No:5WK97262 OE#:476880088, 84422747 Application: Case IH
-
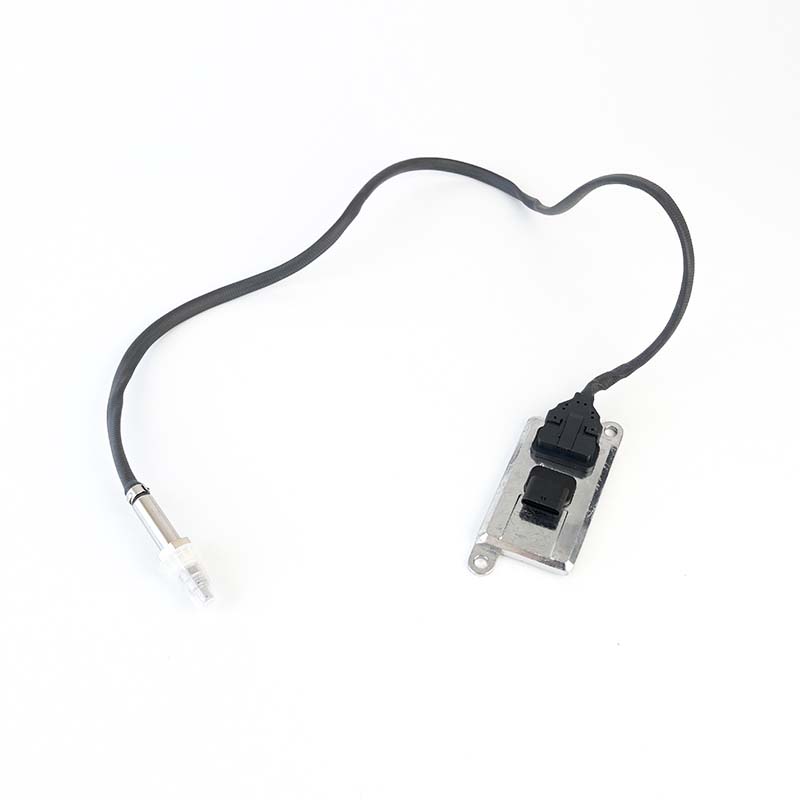 84414466,84292579 NOx Sensor
84414466,84292579 NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX329 Continenal No:5WK96711C OE#:84414466, 84292579 Application: Case IH
-
 ME229792 NOx Sensor
ME229792 NOx SensorSOOK#:SKNOX385B Continenal No:5WK96680 OE#:ME229792 Application: FUSO
Specializing in the research and development of intelligent vehicle exhaust temperature sensor, intelligent NOX sensor, NH3 sensor, H2 sensor and speed sensor, design, production, sales and integration.
Sook High Tech (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. was established in 2015, with a registered capital of 30.5 million yuan. Has won High-tech enterprise, National science and technology small and medium-sized enterprise, Software enterprise, Member of China Machinery Industry Standardization Technology Association, Council Members of Sensor and IoT Industry Association, Council Members of China Instrument Industry Association Sensor Branch and Council Members of Jiangsu Import and Export Chamber of Commerce.
As a professional China OEM NOx Sensor Manufacturers and ODM NOx Sensor Factory
, SOOK High Tech focuses on the design, production, sales and integration of various sensors for smart cars and industrial fields, as well as cables and heaters for the industrial field.
Has an annual production capacity of 600,000 sensors of various types. There are more than 2,000 items of exhaust temperature sensors, 450 items of NOx sensors, and 1,300 items of ABS sensor, which are exported to Europe and the United States.
Learn about our industry exhibition information and recent events in our company.
-
How to Deploy an Ammonia Sensor in Agriculture?
Best Practices for Deploying Ammonia Sensors in Agriculture: 1. Monitoring Point Layout: Deploy Ammonia Sensors at ventilation openings, manure accumulation areas, and feed storage...28 -
How to Properly Install an NH3 Sensor?
Proper Installation of an NH3 Sensor 1. Select a Suitable Installation LocationInstall the Ammonia Sensor at a high point or near the gas inlet where ammonia leaks may occur, such ...21 -
What impact does the PTCEGT sensor have on emission control?
1. Accurate Temperature Monitoring Improves Combustion Efficiency Real-time Temperature Feedback: The PTC EGT sensor utilizes the positive temperature change characteristic of plat...14 -
What is an NTC EGT Sensor?
1. Working Principle The NTC EGT Sensor uses NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistor technology, where the resistance drops rapidly as the temperature rises. When the tem...07
What reset or learning steps are required after replacing a NOx sensor?
1. Clear fault codes and perform a system reset
After replacing a sensor, first use a professional diagnostic tool to read and clear the existing NOx sensor fault codes to ensure the ECU can receive the new sensor's signal.
2. Perform the sensor calibration (learning) procedure
Use the diagnostic tool to access the calibration menu of the emission control system and perform "sensor learning" or "adaptation" according to the manufacturer's instructions. This will allow the ECU to quickly establish a baseline NOx concentration under different operating conditions.
3. Conduct a road test to verify
After completing the reset and learning process, conduct a road test of at least 10 km to monitor exhaust NOx data for stability and confirm that the sensor response time (<1400ms) meets specifications.
4. Recheck the electrical connections
After the road test, recheck the tightness of the sensor connector, wiring harness, and heater circuit to prevent loosening caused by vibration from triggering the fault again.
Why does carbon deposits/soot cause NOx sensor failure? 1. Probe Surface Contamination
After long-term operation, carbon residue and soot in the exhaust gas can deposit on the sensor probe surface, preventing direct gas contact with the sensor element and causing signal attenuation or distortion.
2. Intake Passage Blockage
Carbon deposits can block the sensor's air inlet, reducing airflow and increasing sensor response time, even leading to zero readings.
3. Chemical Corrosion and Electrode Aging
Sulfides and metal particles contained in soot can corrode the electrodes of electrochemical NOx sensors, accelerating component aging and leading to sensor failure.
4. Poor Heat Dissipation
The carbon layer can reduce the sensor's heat dissipation efficiency, causing the operating temperature to rise abnormally, further accelerating the aging and failure of the sensor's internal materials.


 English
English Español
Español Français
Français
 简体中文
简体中文