ADD: Changjiang Road, Gaoyou Economic Development Zone, Jiangsu Province, 225600, China(within the Technology Innovation Center)
MERCEDES-BENZC-CLASS (W203) (2000/05 - 2007/08)MERCEDES-BENZC-CLASS Coupe (CL203) (2001/03 - 2011/06...
See DetailsContent
Automotive sensors detect physical conditions such as temperature, pressure, speed, and chemical composition, convert them into electrical signals, and send them to a vehicle's control unit. These signals allow modern vehicles to optimize performance, improve safety, and operate efficiently in real time.
In modern vehicles, sensors act as the nervous system of the car. Without them, engine management, braking systems, driver assistance technologies, and emissions control would not function reliably.
Automotive sensors are central to vehicle intelligence. Today's cars contain dozens — sometimes hundreds — of sensors that continuously transmit live data to onboard computers. This constant feedback enables real-time system adjustments.
As vehicles become electrified and connected, sensor accuracy becomes even more critical.
Automotive sensors are categorized based on their function. Each type supports a specific subsystem inside the vehicle.
| Sensor Type | Primary Function | Example Use |
| Temperature Sensors | Monitor heat levels | Engine cooling |
| Pressure Sensors | Measure fluid/air pressure | Fuel system |
| Speed Sensors | Track rotation | ABS braking |
| Position Sensors | Detect component location | Throttle control |
| Chemical Sensors | Analyze exhaust gases | Emission systems |
The chart below illustrates how different automotive sensor categories contribute to modern vehicle systems. Engine and safety sensors remain dominant, while EV and ADAS sensors continue to grow as smart mobility expands.
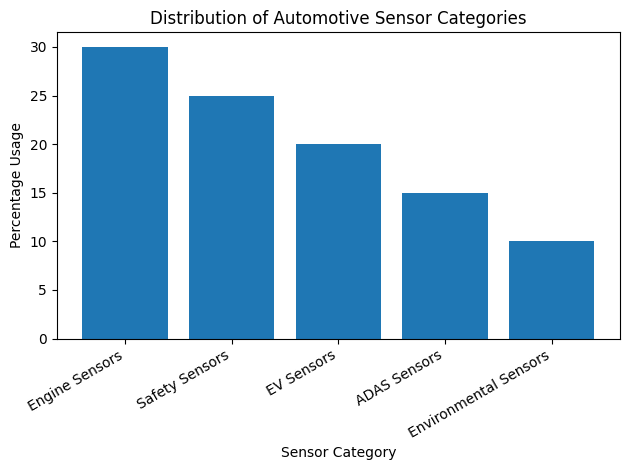
Figure: Distribution of automotive sensor categories in modern vehicles
Most automotive sensors follow a consistent operating cycle:
This feedback loop operates thousands of times per second to maintain vehicle stability.
Safety technologies depend heavily on sensor precision. Sensors detect risks faster than human reaction time.
Electric vehicles contain more sensors than traditional cars. Battery monitoring, motor efficiency, and power management depend on precision measurement. Autonomous systems rely on lidar, radar, and ultrasonic sensor networks to interpret surroundings.
The future of transportation is sensor-driven.
Even small measurement errors can lead to fuel inefficiency, emissions violations, safety risks, or mechanical damage. High-precision sensors ensure consistent performance over millions of operating cycles.
Q: How many sensors are in a modern car?
A: Most vehicles contain 60–100+ sensors depending on system complexity.
Q: Do sensors wear out?
A: Yes. Heat, vibration, and contamination can degrade sensors over time.
Q: Can a car run without sensors?
A: Modern vehicles depend on sensors; failure triggers warning systems.
Q: Are sensors important for EVs?
A: Even more important — EV systems require constant monitoring.
Automotive sensors transform physical conditions into digital intelligence. They enable modern vehicles to operate safely, efficiently, and autonomously. As electrification and automation accelerate, sensor technology will define the future of mobility.